Search Our Database
How to backup/restore MySQL database with mysqldump command
Introduction
The mysqldump utility is a powerful tool designed to back up MySQL databases and transfer data to another MySQL server. This utility generates a set of SQL statements that can be used to recreate the original database on a different server or after a failure. Whether you’re migrating a database or performing regular backups, this tool helps safeguard against data loss.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- SSH access to the Server.
- MySQL login credentials.
1. Backing Up a Database
To back up a database, use the following command:
mysqldump -u [database_username] -p [database_name] > [database_backup_file.sql]
Example:
If username is ips1_user and the database is ips1_db, the command would look like this:
mysqldump -u ips1_user -p ips1_db > ips1_db_backup.sql
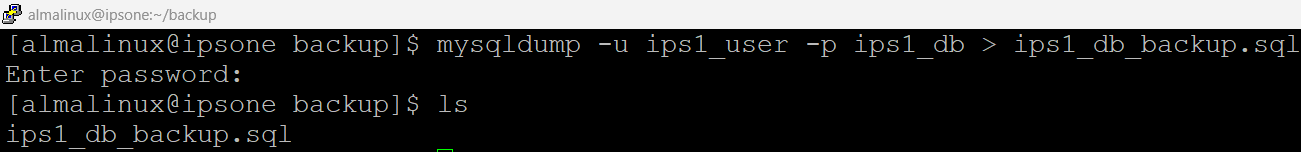
Here’s a breakdown of each part of the mysqldump command:
- -u [database_username]: The username used to connect to the MySQL server.
- -p: Prompts for the password of the specified database username.
- [database_name]: The name of the database you wish to back up.
- >: Redirects the output to the specified file.
- [database_backup_file.sql]: The file where the backup will be saved.
2. Transfer the database to another Server
If you need to restore the database on a different server, you will first need to transfer the backed-up database to that server. This can be done by using SCP command can be used to securely transfer the MySQL backup file between servers.
scp [source_file] [username]@[remote_server]:[destination_path]
Example:
To transfer ips1_database_backup.sql from your current server to another server:
scp ips1_database_backup.sql root@192.168.1.10:/path/to/destination/
Here’s a breakdown of each part of the scp command:
- [source_file]: The file you want to transfer (e.g., ips1_database_backup.sql).
- [username]: The username of the remote server.
- [remote_server]: The IP address or hostname of the destination server.
- [destination_path]: The folder on the remote server where the file will be copied (e.g., /path/to/destination/).
3. Restoring a Database
To restore a database, use the following command. This will overwrite the existing database with the backup data:
mysql -u [database_username] -p [database_name] < [database_backup_file.sql]
Example:
If username is ips1_user and the database is ips1_db, the command would look like this:
mysql -u ips1_user -p ips1_db < ips1_db_backup.sql

Here’s a breakdown of the restore command:
- -u [database_username]: The username used to connect to the MySQL server.
- -p: Prompts for the password of the specified database username.
- [database_name]: The database you want to restore.
- < [database_backup_file.sql]: Redirects the backup file into the MySQL database.
Note: Ensure you have a backup of your existing database before restoring, as this operation will replace all current data.
Conclusion
Using the mysqldump command provides a simple and effective way to back up and restore your MySQL databases. Always ensure you have a backup of your existing database before performing any restoration to prevent data loss.