Search Our Database
How to run Traceroute using Command Prompt in Windows
Introduction
Traceroute is a network diagnostic tool that traces the path data takes from your device to a destination server. It identifies each hop along the route and measures the time taken for the data to travel between points, helping to diagnose connection issues. This guide will show you how to run a traceroute using Command Prompt on Windows to troubleshoot connectivity problems.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- A Windows-based computer.
- The IP address or domain name of the destination server.
Step-by-Step Guide
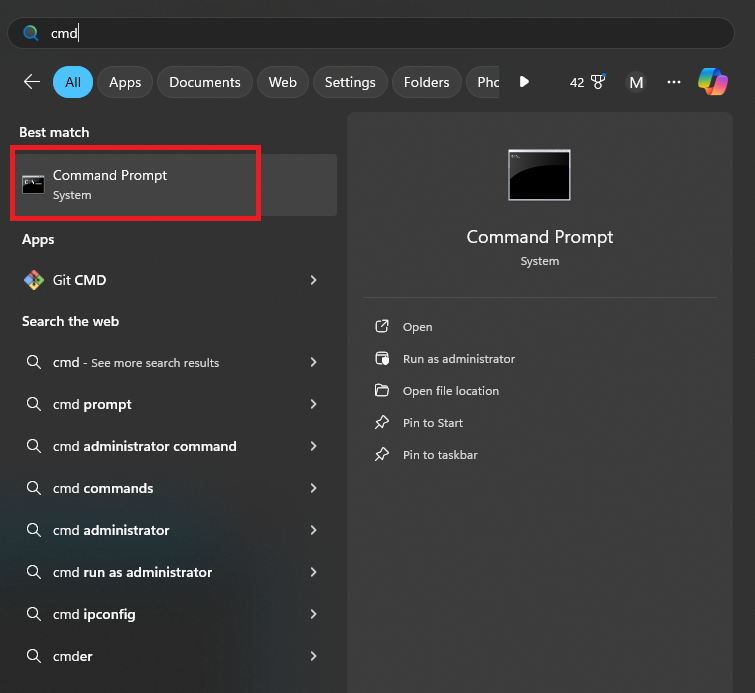
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- In the search bar, type cmd or Command Prompt.
Step 2: Run the traceroute command
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command:
tracert your_destination_domain_or_IP
- Example:
tracert ipserverone.com
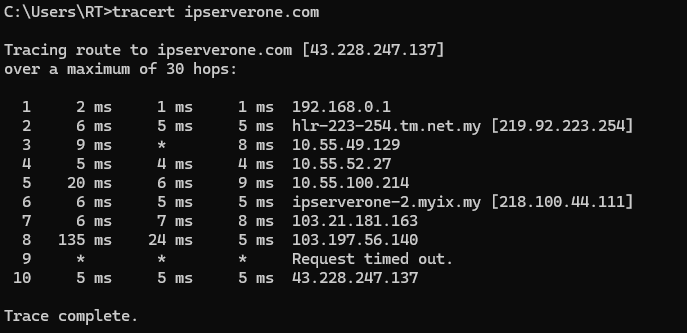
Step 3: Review the traceroute results
- The traceroute command will begin listing each hop between your computer and the destination server.
- Each line displays the following information:
- The hop number.
- The time it took for the data to travel to that hop (in milliseconds).
- The IP address or hostname of the device at that hop.
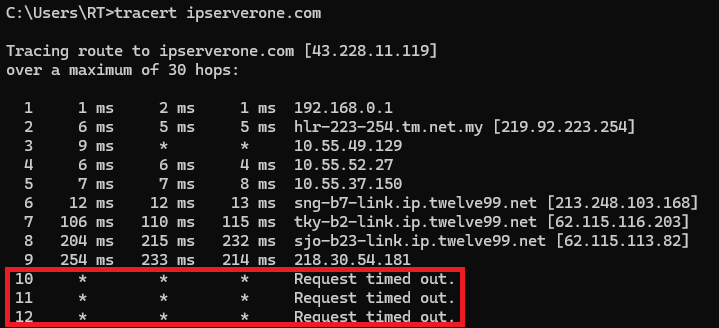
If the destination server is reached, the traceroute will stop. If there are connection issues, you may see lines with “Request timed out,” which indicates a problem at that hop.
Step 4: Analyze the results
- If all hops complete successfully, you will see the destination IP or hostname at the end of the list.

- If some hops time out or take too long, it may indicate a network issue that you need to investigate further.
Conclusions
Traceroute is a useful tool for diagnosing network problems, identifying where delays or packet loss occur along the route to a destination server. By using the Command Prompt in Windows, you can quickly check the health of your connection. If issues persist, you may need to reach out to your network administrator or hosting provider.