Search Our Database
Understanding the Differences Between Dedicated (Bare Metal) Servers and Cloud Servers
What is a Dedicated (Bare Metal) Server?
A dedicated server, also known as a bare-metal server, is a physical piece of hardware equipped with components such as a processor, RAM, and hard drives. This type of server is entirely dedicated to a single user or organization, providing complete control over its resources and configurations.
What is a Cloud Server?
Cloud servers, or virtual machines (VMs), function as servers but do not consist of physical components. Instead, VMs exist in a virtual format and run on dedicated servers. This process of creating virtual machines is called virtualization and is managed through a hypervisor, which is software that creates and runs VMs. Virtualization allows:
- Multiple VMs to run on a single dedicated server.
- Resources on a dedicated server to be divided among several VMs.
Virtualization vs. Dedicated Server
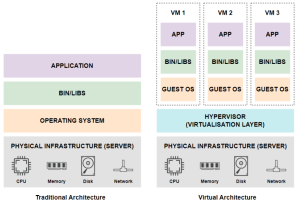
Traditional Architecture (Dedicated Server):
- A dedicated server has a single operating system installed directly onto the physical hardware.
- Applications are installed on top of the OS.
- All applications must be compatible with the same software stack.
Virtual Architecture (Cloud Server):
- A hypervisor is installed directly on the physical server, replacing the operating system.
- Multiple VMs can be created on the hypervisor, each with its own guest OS, binaries, and libraries.
Types of Hypervisors
- Type 1 Hypervisor: Runs directly on the physical server, introducing a small resource overhead (around 10%).
- Type 2 Hypervisor: Runs on top of an operating system installed on the physical hardware, resulting in a larger performance overhead and higher costs.
Benefits of Virtualization
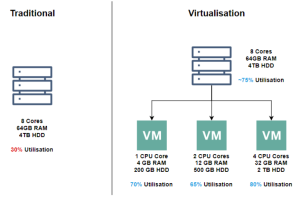
1. Efficient Use of Server Resources
- Dedicated servers are single-user, leading to potential resource inefficiency.
- Virtualization allows multiple users to share resources on a single dedicated server, allocating resources according to specific needs.
2. Speed, Flexibility, and Scalability
- Dedicated servers require more time to set up.
- VMs can be created or destroyed in minutes, enabling quick service delivery.
- VMs can be scaled up or down rapidly to match changing demands.
3. Hardware Independence and VM Portability
- VMs are independent of the underlying hardware, allowing them to run different OS types.
- VMs can be moved between servers without needing changes to device drivers, OS, or applications, facilitating easier migrations.
4. Easier Backups and System Recovery
- Cloud environments offer quick snapshot capabilities for VMs.
- Snapshots provide point-in-time copies and are faster to restore compared to traditional server backups, minimizing downtime.
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
Public Cloud:
- Owned and operated by third-party providers (e.g., IP ServerOne).
- Resources are shared among multiple clients.
- Follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
- Highly scalable with on-demand resource provisioning.
Private Cloud:
- Owned and operated by a single organization.
- Resources are dedicated to one client.
- Offers greater control over security, compliance, and custom configurations.
- Involves higher upfront costs but provides tailored infrastructure.
Conclusion
IP ServerOne leverages virtualization technology in its Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) offerings, providing efficient, flexible, and scalable cloud computing solutions. Virtualization enhances server resource utilization, speeds up deployment times, and simplifies system management and recovery processes.